This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
WIRELESS ACCESS DEPLOYMENT
Deploy and Configure Wireless APs
Follow these steps to deploy and configure your wireless APs:
- Specify Wireless AP Channel Frequencies
- Configure Wireless APs
Specify Wireless AP Channel Frequencies
When you deploy multiple wireless APs at a single geographical site, you must configure wireless APs that have overlapping signals to use unique channel frequencies to reduce interference between wireless APs.
You can use the following guidelines to assist you in choosing channel frequencies that do not conflict with other wireless networks at the geographical location of your wireless network.
- If there are other organizations that have offices in close proximity or in the same building as your organization, identify whether there are any wireless networks owned by those organizations. Find out both the placement and the assigned channel frequencies of their wireless AP's, because you need to assign different channel frequencies to your AP's and you need to determine the best location to install your AP's.
- Identify overlapping wireless signals on adjacent floors within your own organization. After identifying overlapping coverage areas outside and within your organization, assign channel frequencies for your wireless APs, ensuring that any two wireless APs with overlapping coverage are assigned different channel frequencies.
Configure Wireless APs
Use the following information along with the product documentation provided by the wireless AP manufacturer to configure your wireless APs.
This procedure enumerates items commonly configured on a wireless AP. The item names can vary by brand and model and might be different from those in the following list. For specific details, see your wireless AP documentation.
To configure your wireless APs
- SSID. Specify the name of the wireless network(s) (for example, ExampleWLAN). This is the name that is advertised to wireless clients.
- Encryption. Specify WPA2-Enterprise (preferred) or WPA-Enterprise, and either AES (preferred) or TKIP encryption cipher, depending on which versions are supported by your wireless client computer network adapters.
- Wireless AP IP address (static). On each AP, configure a unique static IP address that falls within the exclusion range of the DHCP scope for the subnet. Using an address that is excluded from assignment by DHCP prevents the DHCP server from assigning the same IP address to a computer or other device.
- Subnet mask. Configure this to match the subnet mask settings of the LAN to which you have connected the wireless AP.
- DNS name. Some wireless APs can be configured with a DNS name. The DNS service on the network can resolve DNS names to an IP address. On each wireless AP that supports this feature, enter a unique name for DNS resolution.
- DHCP service. If your wireless AP has a built-in DHCP service, disable it.
- RADIUS shared secret. Use a unique RADIUS shared secret for each wireless AP unless you are planning to configure APs as RADIUS Clients in NPS by group. If you plan to configure APs by group in NPS, the shared secret must be the same for every member of the group. In addition, each shared secret you use should be a random sequence of at least 22 characters that mixes uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and punctuation. To ensure randomness, you can use a random character generator, such as the random character generator found in the NPS Configure 802.1X wizard, to create the shared secrets.
- RADIUS server IP address. Type the IP address of the server running NPS.
- UDP port(s). By default, NPS uses UDP ports 1812 and 1645 for authentication messages and UDP ports 1813 and 1646 for accounting messages. It is recommended that you use these same UDP ports on your APs, but if you have a valid reason to use different ports, ensure that you not only configure the APs with the new port numbers but also reconfigure all of your NPSs to use the same port numbers as the APs. If the APs and the NPSs are not configured with the same UDP ports, NPS cannot receive or process connection requests from the APs, and all wireless connection attempts on the network will fail.
- VSAs. Some wireless APs require vendor-specific attributes (VSAs) to provide full wireless AP functionality. VSAs are added in NPS network policy.
- DHCP filtering. Configure wireless APs to block wireless clients from sending IP packets from UDP port 68 to the network, as documented by the wireless AP manufacturer.
- DNS filtering. Configure wireless APs to block wireless clients from sending IP packets from TCP or UDP port 53 to the network, as documented by the wireless AP manufacturer.
Create Security Groups for Wireless Users
Follow these steps to create one or more wireless users security groups, and then add users to the appropriate wireless users security group:
- Create a Wireless Users Security Group
- Add Users to the Wireless Security Group
Create a Wireless Users Security Group
You can use this procedure to create a wireless security group in the Active Directory Users and Computers Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in.
Membership in Domain Admins, or equivalent, is the minimum required to perform this procedure.
To create a wireless users security group
1. Click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users and Computers. The Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in opens. If it is not already selected, click the node for your domain. For example, if your domain is example.com, click example.com.
2. In the details pane, right-click the folder in which you want to add a new group (for example, right-click Users), point to New, and then click Group.
3. In New Object – Group, in Group name, type the name of the new group. For example, type Wireless Group.
4. In Group scope, select one of the following options:
- Domain local
- Global
- Universal
5. In Group type, select Security.
6. Click OK.
If you need more than one security group for wireless users, repeat these steps to create additional wireless users groups. Later you can create individual network policies in NPS to apply different conditions and constraints to each group, providing them with different access permissions and connectivity rules.
Add Users to the Wireless Users Security Group
You can use this procedure to add a user, computer, or group to your wireless security group in the Active Directory Users and Computers Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in.
Membership in Domain Admins, or equivalent is the minimum required to perform this procedure.
To add users to the wireless security group
1. Click Start, click Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users and Computers. The Active Directory Users and Computers MMC opens. If it is not already selected, click the node for your domain. For example, if your domain is example.com, click example.com.
2. In the details pane, double-click the folder that contains your wireless security group.
3. In the details pane, right-click the wireless security group, and then click Properties. The Properties dialog box for the security group opens.
4. On the Members tab, click Add, and then complete one of the following procedures to either add a computer or add a user or group.
To add a user or group
1. In Enter the object names to select, type the name of the user or group that you want to add, and then click OK.
2. To assign group membership to other users or groups, repeat step 1 of this procedure.
To add a computer
1. Click Object Types. The Object Types dialog box opens.
2. In Object types, select Computers, and then click OK.
3. In Enter the object names to select, type the name of the computer that you want to add, and then click OK.
4. To assign group membership to other computers, repeat steps 1-3 of this procedure.
Configure Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies
Follow these steps to configure Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies Group Policy extension:
- Open or Add and Open a Group Policy Object
- Activate Default Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies
- Configure the New Wireless Network Policy
Open or Add and Open a Group Policy Object
By default, the Group Policy Management feature is installed on computers running Windows Server 2016 when the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) server role is installed and the server is configured as a domain controller. The following procedure that describes how to open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) on your domain controller. The procedure then describes how to either open an existing domain-level Group Policy object (GPO) for editing, or create a new domain GPO and open it for editing.
Membership in Domain Admins, or equivalent, is the minimum required to perform this procedure.
To open or add and open a Group Policy object
1. On your domain controller, click Start, click Windows Administrative Tools, and then click Group Policy Management. The Group Policy Management Console opens.
2. In the left pane, double-click your forest. For example, double-click Forest: example.com.
3. In the left pane, double-click Domains, and then double-click the domain for which you want to manage a Group Policy object. For example, double-click example.com.
4. Do one of the following:
- To open an existing domain-level GPO for editing, double click the domain that contains the Group Policy object that you want to manage, right-click the domain policy you want to manage, such as the Default Domain Policy, and then click Edit. Group Policy Management Editor opens.
- To create a new Group Policy object and open for editing, right-click the domain for which you want to create a new Group Policy object, and then click Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here.
In New GPO, in Name, type a name for the new Group Policy object, and then click OK.
Right-click your new Group Policy object, and then click Edit. Group Policy Management Editor opens.
In the next section you will use Group Policy Management Editor to create wireless policy.
Activate Default Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies
This procedure describes how to activate the default Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies by using the Group Policy Management Editor (GPME).
Membership in Domain Admins, or equivalent, is the minimum required to perform this procedure.
To activate default Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies
1. Follow the previous procedure, To open or add and open a Group Policy object to open the GPME.
2. In the GPME, in the left pane, double-click Computer Configuration, double-click Policies, double-click Windows Settings, and then double-click Security Settings.
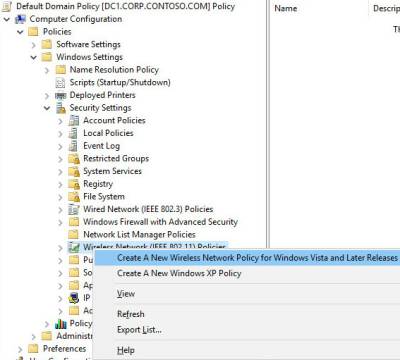
3. In Security Settings, right-click Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies, and then click Create a new Wireless Policy for Windows Vista and Later Releases.
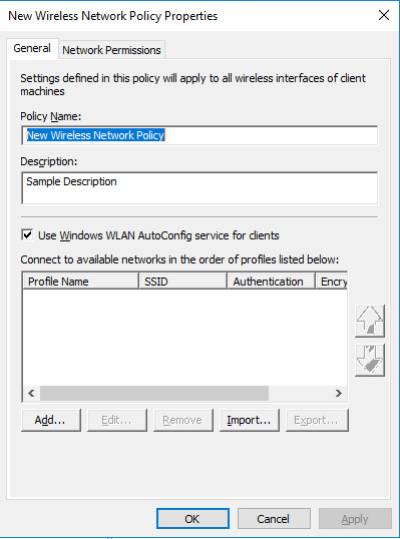
4. The New Wireless Network Policy Properties dialog box opens. In Policy Name, type a new name for the policy or keep the default name. Click OK to save the policy. The default policy is activated and listed in the details pane of the GPME with the new name you provided or with the default name New Wireless Network Policy.
5. In the details pane, double-click New Wireless Network Policy to open it.
In the next section you can perform policy configuration, policy processing preference order, and network permissions.