This is an old revision of the document!
VLAN (VIRTUAL AREA NETWORKS)
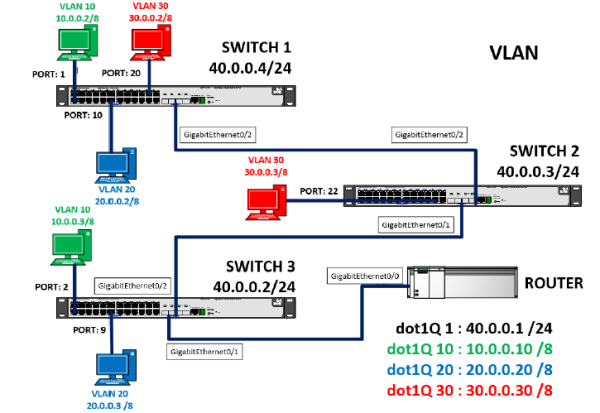
A VLAN (802.1Q), an acronym for virtual LAN (virtual local area network), is a method of creating independent logical networks within the same physical network. Multiple VLANs can coexist on a single physical switch or on a single physical network. They are useful for reducing the size of the broadcast domain and help in network administration, separating logical segments of a local area network (workspaces, common applications, administrative or production departments, etc.) that should not interchange data using the local network (although they could do so through a router or Layer 3 switch).
In itself, a VLAN can be formed by two computer networks that are connected, in a physical sense, to different segments of a LAN network, but which nevertheless act as if they were attached to the same port. This is because they have the same VLAN ID and make up a single Broadcast domain. The maximum number of VLAN IDs possible to implement is 4096.
There are several ways to establish a VLAN. Level 1 VLANs are those that are developed from the use of ports. Layer 2 VLANs are created through the assignment of MAC addresses or by protocol type and Layer 3 VLANs, which involve the creation of IP subnets.
There is also another type of VLAN called QinQ, it is an L2 technology for operators or large companies that have a backbone based on L2 allowing them to encapsulate a VLAN identifier (ID) (IEEE 802.1Q) in another 802.1Q identifier (ID). This is a practical approach to supporting clients with multiple VLANs using a single VLAN ID to be transported across a given backbone. QinQ offers from 4096 VLANs (12 bits), up to 16.8 million VLANs (4096 x 4096, 24 bits) in total.